Diabetes is a long-term metabolic disorder that results in high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can cause severe harm to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, usually affecting adults. It occurs when the body resists insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. In the last 30 years, the incidence of type 2 diabetes has significantly increased in countries of all income levels.
Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. For people with diabetes, access to affordable treatment, especially insulin, is crucial. There is a global goal to stop the rise of diabetes and obesity by 2025.
Prevalence and Impact of Diabetes
Currently, around 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, with most living in low- and middle-income countries. Diabetes directly causes 1.5 million deaths each year. The number of diabetes cases and its prevalence have been rising steadily over recent decades.
Recognizing Symptoms of Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes symptoms often appear suddenly and include:
– Frequent urination
– Intense thirst
– Constant hunger
– Weight loss
– Vision changes
– Fatigue
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes symptoms are similar but usually less noticeable. This can lead to a diagnosis only after complications have developed. Therefore, recognizing risk factors is essential.
Preventing and Managing Diabetes
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
While type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, effective strategies exist to prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications. These strategies include:
– Regular exercise
– Healthy eating habits
– Avoiding smoking
– Managing blood pressure and lipid levels
These practices, when implemented in schools, homes, and workplaces, promote good health for everyone.
Early Diagnosis and Ongoing Care
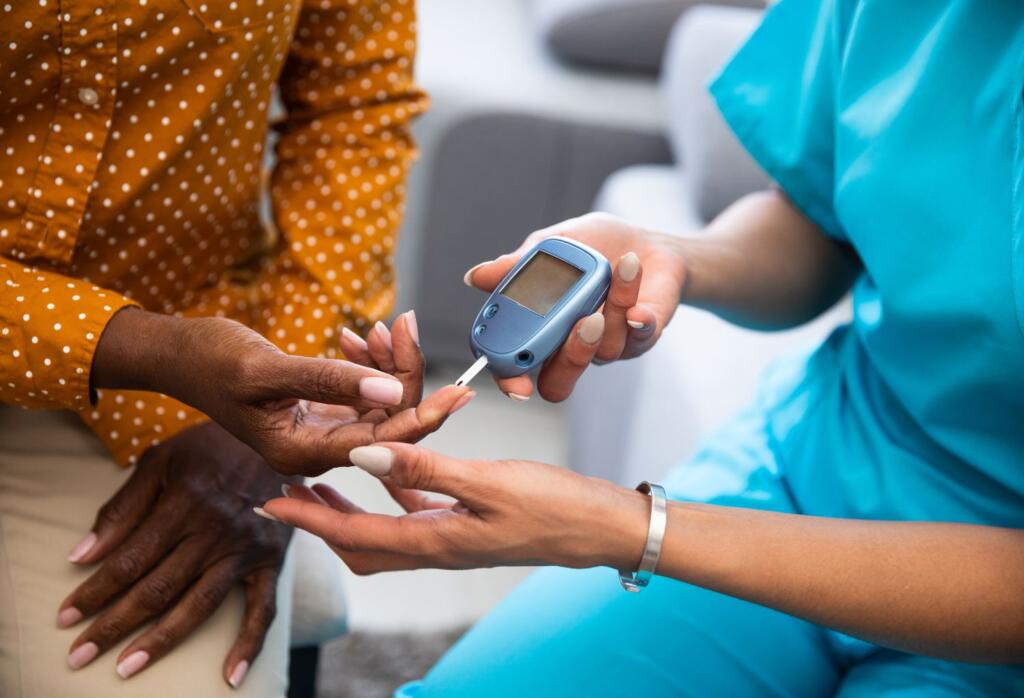
Early diagnosis is vital for managing diabetes. The longer diabetes remains undiagnosed and untreated, the worse the health outcomes. Therefore, easy access to basic diagnostics like blood glucose testing should be available in primary health care settings. Patients also need regular specialist assessments or treatments for complications.
Effective Interventions for Diabetes Management
A series of cost-effective measures can significantly improve outcomes for diabetes patients, regardless of the type. These interventions include:
– Blood glucose control through diet, physical activity, and medication if necessary
– Blood pressure and lipid management to reduce cardiovascular risks and other complications
– Regular screening for damage to the eyes, kidneys, and feet to enable early treatment
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels. Developing a healthy eating plan, participating in regular physical activity, and adjusting insulin therapy with the help of a diabetes care team can help reduce health risks.
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes can lead to several complications, such as:
– Vision problems
– High blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke
– Kidney damage
– Nerve damage
– Skin sores and infections, which can cause pain and tissue death
Following proper dietary guidelines can mitigate these difficulties and improve overall quality of life.
Preparing a Diabetes-Friendly Eating Plan
There is no one-size-fits-all diabetes diet. A registered dietitian or nutritionist can help create a personalized eating plan that fits individual preferences and lifestyles.
Tips for a Diabetes Eating Plan
– Plan meals ahead of time, grocery shop, and prepare meals at home to save money and meet diabetes goals.
– A well-stocked kitchen with healthy food can reduce unnecessary sugar, carbohydrates, sodium, and fat that can spike blood sugar.
– Consistency is key: don’t skip meals, match insulin to your eating schedule, and pay attention to food labels.
When short on time, choose fast foods or convenience foods that fit your eating plan. Many chain restaurants provide nutritional information online, making it easier to choose suitable options, such as a salad with grilled chicken or fajitas with vegetables and a sugar-free beverage.
By following these guidelines, managing diabetes can become more straightforward and effective, leading to better health outcomes and quality of life.
ALSO READ: The life hack that can cure Diabetes Type 2