China was trying to encircle India through the String of Pearls. The country made a strong presence in the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, and the Bay of Bengal through its debt trap port capturing diplomacy. But the strategic counter from India not only defeated the Chinese sinister plan but also brought China to such a situation that they feared for their own security in the region.
BRI & String of Pearls
In its aggressive push for expanding footprints in the strategic location by ‘capturing’ strategic ports through ‘debt trap diplomacy’ in the region, China is building dual-use ports in India’s neighbourhood. In consonance with its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China is trying to revive the ancient silk route to market its product and under the veil of business opportunities, it has captured several ports in the region.
Moreover, the country has already captured the strategic port location in the region through its debt-trap diplomacy. The Doraleh multipurpose port in Djibouti, Gwadar & Karachi Deepwater port in Pakistan, Hambantota & CICT Terminal in Sri Lanka and Kyaukpyu port in Myanmar have already been completed.
The goal is to increase its presence on the choke points of major maritime trade routes like the Strait of Mandeb, the Strait of Malacca, the Strait of Hormuz, and the Lombok Strait.
Read More: How India’s ‘Necklace of Diamonds’ outsmarted China’s ‘String of Pearls’ in the Indian Ocean
Double Fish Hook Strategy
The Indo-Pacific maritime trade route is called a Global Highway as it contributes to 40% of global trade and 62% of the world’s GDP. It is a highway through which the majority of the oil and cargo passes. So, it becomes very important to maintain peace and tranquillity on the Global Highway. It becomes a global responsibility to maintain peace and tranquillity in the region to strengthen the supply chain.
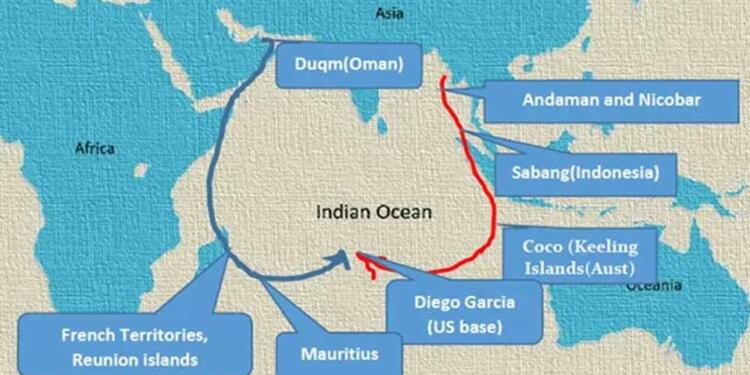
To strengthen our position in the region and counter any potential threat in the maritime trade, India is forming regional military alliances to secure the Global Highway route. With its policy of Necklace of Diamonds, the country has launched another strategic policy called Double Fish Hook.
One of the fish hooks expands around the Eastern Indian Ocean region. It originates from Indian Islands Andaman & Nicobar, in the middle of the Sabang port in Indonesia and extends to the Cocos Islands of Australia, and ends at Diego Garcia, the US military base in the Chagos archipelago.
Further, the second hook expands around the Western Indian Oceans. It starts the Duqm port in Oman, the Reunion Island of French territories, and other small island groups of Mauritius and again ends at Diego Garcia.
Also Read: India joins a trade pact that will starve China of money
To consolidate the position and formally realize the strategy on the ground, India has not only strengthened its navy presence but has also signed various agreements with different countries. It includes:-
- At the Andaman & Nicobar Islands, India has deployed a strong tri-service theatre command.
- India has also secured strategic access to the Indonesian Sabang port which forms the choke point of Malacca Strait and the route of about 40% of India’s trade.
- In June 2020, India signed a Mutual Logistics Support Agreement (MLSA) with Australia. It facilitated reciprocal access to military logistics facilities and improved interoperability between the two nations.
- In February 2018, PM Modi’s visit to Oman resulted in the conclusion of a strategic relationship. A Memorandum of Understanding was signed between the two nations which will allow India to use the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support.
- In March 2018, India-France signed a key agreement that will facilitate the two armed forces to receive logistical support, supplies, and services from each other.
- In March 2015, India signed various ‘Memorandum of Understanding’ with Mauritius for the development of ports and other allied activities.
Further, India signed various agreements with the United States of America for the reciprocal use of resources. The agreements include:-
- The Logistics Support Agreement (LSA)
- Communication Interoperability and Security Memorandum of Agreement (CISMOA)
- Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement for Geo-spatial Cooperation (BECA)
- Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA)
These agreements will not only secure the mutual use of respective military bases for logistical agreements but also enable sharing of intelligence data between the two countries. Further, this will also allow India to use the strategically located American military base in the Indian Ocean.
It is very important to understand that these strategic alliances with regional countries converge with the Indian Necklace of Diamonds. About 80% of China’s imported oil passes through the Indian Ocean and Malacca Strait. Andaman & Nicobar Islands of India and Sabang port of Indonesia is at the choke point of the Global Highway. Further, the strategic military presence and grouping have choked the Chinese plan, and it seems like India has nabbed the neck of the paper dragon through its smart diplomacy.