Understanding the Concept of Rayleigh Jeans Radiation Law
The Rayleigh Jeans Radiation Law, which was developed in the early 20th century, was instrumental in providing modern quantum mechanics with an explanation of how objects emit radiation at different temperatures.
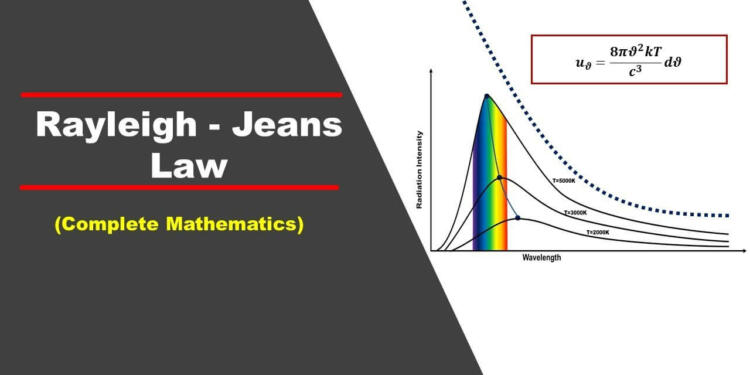
Rayleigh Jeans Radiation Law Concept
An ancient scientific theory called the Rayleigh Jeans Radiation Law describes how hot objects emit light. Early in the 20th century, British physicists Sir James Jeans and Lord Rayleigh introduced it. This law made an effort to characterize the quantity of light that a hot object at a specific temperature would emit, especially in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
This law states that the amount of radiation emitted by a hot object is directly proportional to its temperature, or, to put it another way, that the hotter an object gets, the more light it emits. The assumption behind this law is that all objects, regardless of temperature, will continue to emit light as their temperature rises, but experiments and subsequent research have shown that this idea has some limitations.
The Rayleigh-Jeans Radiation Law has a flaw in that it assumes that objects will continue to emit energy forever as they heat up. The actual observations do not align with this prediction. Put another way, the outcomes of applying this law to extremely hot objects did not match what was observed. More precise and thorough theories of radiation, such as Max Planck’s theory of black-body radiation and the ensuing creation of quantum mechanics, were developed as a result of this gap.
The Rayleigh-Jeans Radiation Law was significant in the development of physics even with its flaws. It was the first step toward understanding the behavior of light emitted by heated objects. Due to its limitations, more precise and sophisticated theories were eventually investigated, revolutionizing physics and laying the groundwork for contemporary quantum mechanics.
Also Read: What is A NWD Transaction in A Bank Statement? Detailed Answer
The Rayleigh-Jeans Radiation Law has played a significant role in the history of science, even though it is no longer the most widely accepted theory explaining the behavior of light emitted by hot objects. It reminds us how crucial it is to challenge and improve scientific theories in order to gain a deeper understanding of the natural world.