Welcome, students, parents or teachers in this article we are going to give you answer of which is largest endocrine gland? It’s Functions. Take a note that in exams you can add more points in answer to score more. To earn extra marks you can explain it in about 300 words. Thanks for reading the answer.
Which is largest endocrine gland? It’s Functions
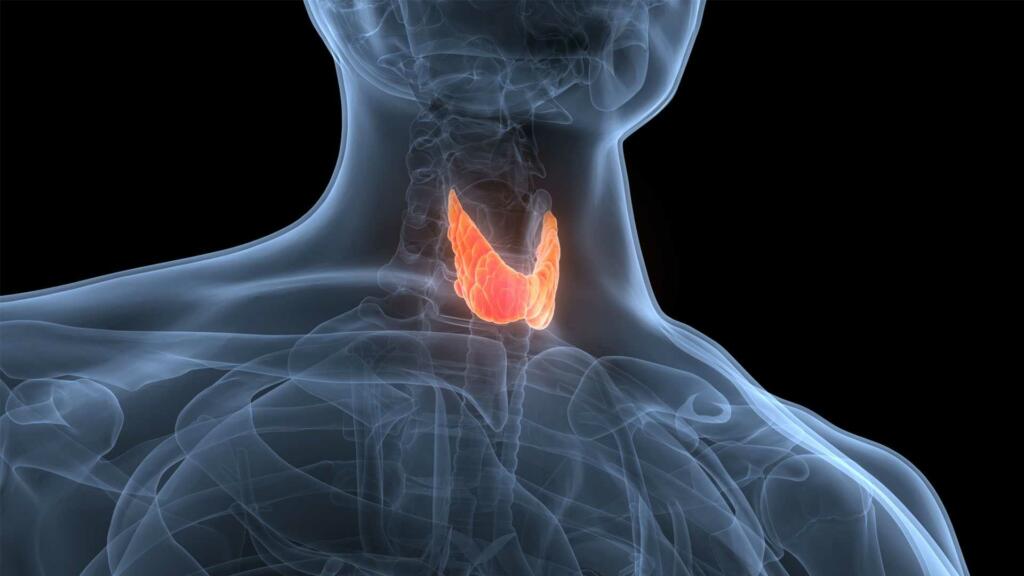
Which is largest endocrine gland: The largest endocrine gland is the thyroid gland. It is located in the neck and produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, including thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the body’s energy levels, heart rate, and body temperature, as well as influencing the growth and development of the brain and nervous system. The thyroid gland also helps to regulate the body’s use of calcium and phosphorus, and helps to keep the body’s metabolism in balance.
The largest endocrine gland in the human body is the thyroid gland. Located in the neck, it produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. These hormones, called thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are released into the bloodstream and travel to different parts of the body, where they interact with cells and organs to control various bodily functions. The thyroid gland also produces calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood. Without proper function of the thyroid gland, metabolism and growth can be disrupted, leading to conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Also Read: Mass of sodium? With Definition of Mass and Sodium
Functions of thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism by producing and releasing hormones that control the body’s energy levels, heart rate, and body temperature.
The two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are regulated by the pituitary gland, which releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to signal the thyroid gland to produce more or less hormones as needed.
When the thyroid gland is functioning properly, it produces just the right amount of T4 and T3 to keep the body’s metabolism in balance. However, if the gland produces too much or too little of these hormones, it can lead to various health problems such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). These conditions can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, and changes in mood or energy levels.
Overall, the thyroid gland plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s metabolism and overall health. Any dysfunction or imbalance in the gland’s hormone production can have a significant impact on the body’s overall well-being.